Tether Developer Guide
Acknowledgements
This project is based on the AddressBook-Level3 project created by the SE-EDU initiative.
Setting up, getting started
Refer to the guide Setting up and getting started.
Design
Architecture
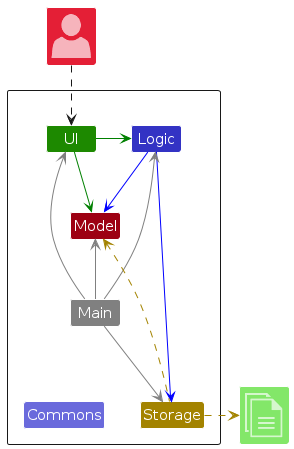
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the App.
Given below is a quick overview of main components and how they interact with each other.
Main components of the architecture
Main (consisting of classes Main and MainApp) is in charge of the app launch and shut down.
- At app launch, it initializes the other components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
- At shut down, it shuts down the other components and invokes cleanup methods where necessary.
The bulk of the app's work is done by the following four components:
UI: The UI of the App.Logic: The command executor.Model: Holds the data of the App in memory.Storage: Reads data from, and writes data to, the hard disk.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
How the architecture components interact with each other
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user issues the command delete 1.
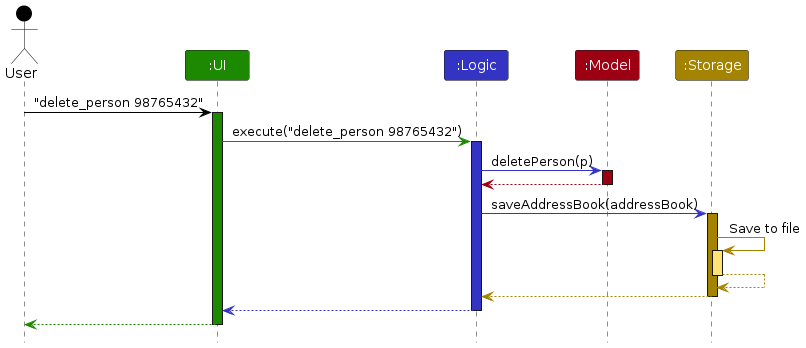
Each of the four main components (also shown in the diagram above),
- defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. - implements its functionality using a concrete
{Component Name}Managerclass (which follows the corresponding APIinterfacementioned in the previous point.
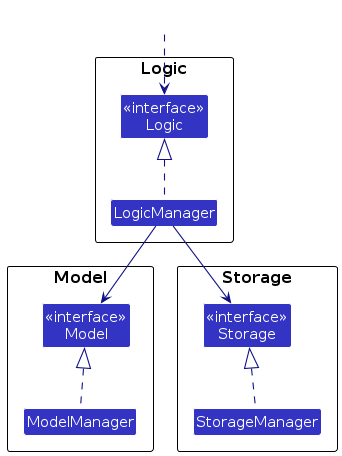
For example, the Logic component defines its API in the Logic.java interface and implements its functionality using the LogicManager.java class which follows the Logic interface. Other components interact with a given component through its interface rather than the concrete class (reason: to prevent outside component's being coupled to the implementation of a component), as illustrated in the (partial) class diagram below.
The sections below give more details of each component.
UI component
The API of this component is specified in Ui.java
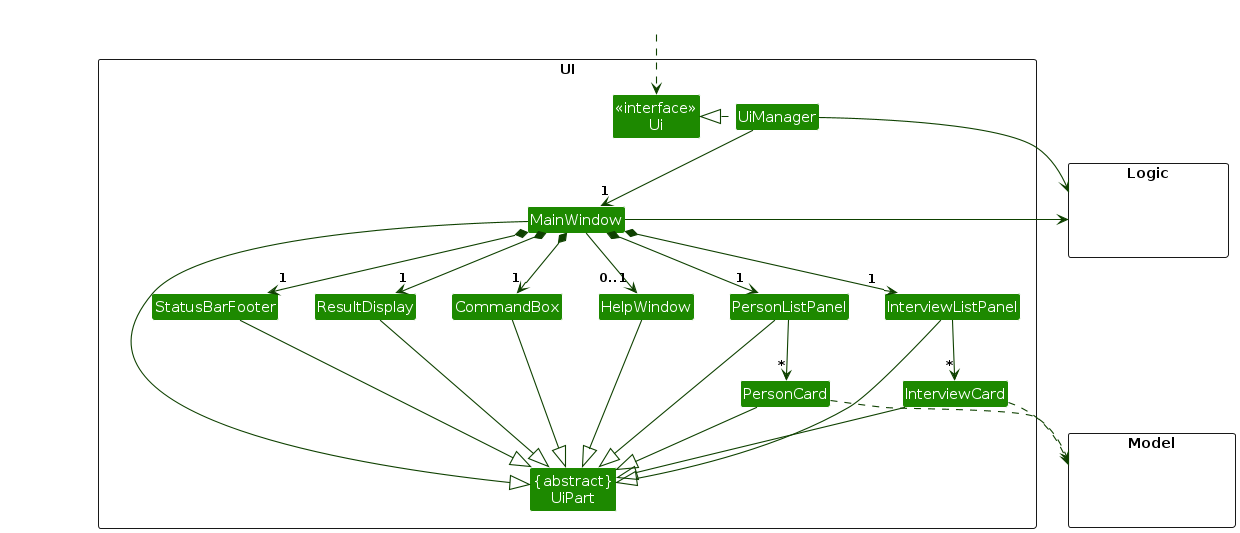
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts e.g.CommandBox, ResultDisplay, PersonListPanel, StatusBarFooter, InterviewListPanel etc. All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class which captures the commonalities between classes that represent parts of the visible GUI.
The UI component uses the JavaFx UI framework. The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder. For example, the layout of the MainWindow is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
- executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. - listens for changes to
Modeldata so that the UI can be updated with the modified data. - keeps a reference to the
Logiccomponent, because theUIrelies on theLogicto execute commands. - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent, as it displaysPersonandInterviewobjects residing in theModel.
Logic component
API : Logic.java
Here's a (partial) class diagram of the Logic component:
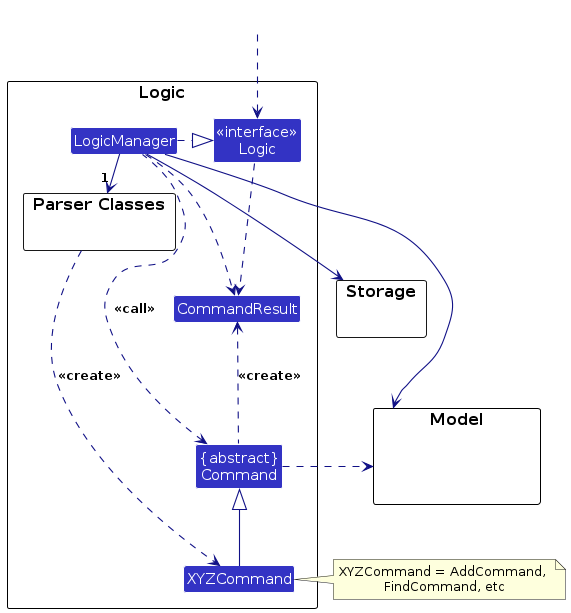
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component, taking execute("delete 1") API call as an example.
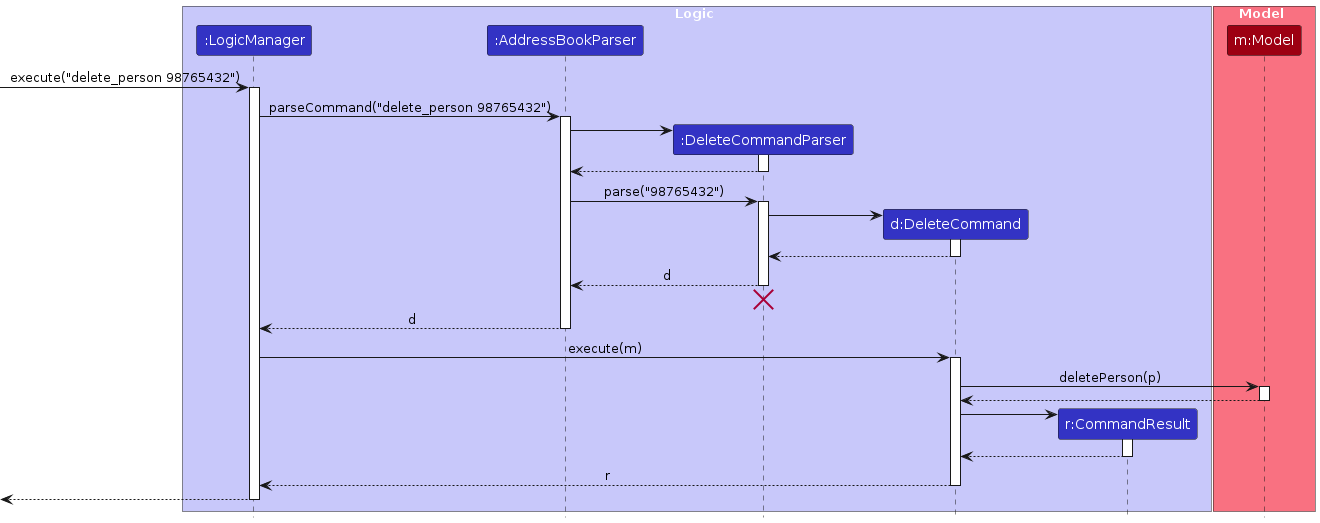
Note: The lifeline for DeleteCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline continues till the end of diagram.
How the Logic component works:
- When
Logicis called upon to execute a command, it is passed to anAddressBookParserobject which in turn creates a parser that matches the command (e.g.,DeleteCommandParser) and uses it to parse the command. - This results in a
Commandobject (more precisely, an object of one of its subclasses e.g.,DeleteCommand) which is executed by theLogicManager. - The command can communicate with the
Modelwhen it is executed (e.g. to delete a person).
Note that although this is shown as a single step in the diagram above (for simplicity), in the code it can take several interactions (between the command object and theModel) to achieve. - The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is returned back fromLogic.
Here are the other classes in Logic (omitted from the class diagram above) that are used for parsing a user command:
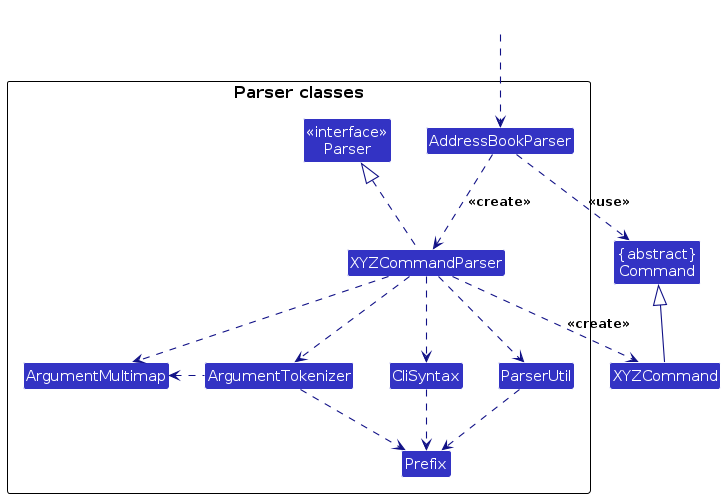
How the parsing works:
- When called upon to parse a user command, the
AddressBookParserclass creates anXYZCommandParser(XYZis a placeholder for the specific command name e.g.,AddCommandParser) which uses the other classes shown above to parse the user command and create aXYZCommandobject (e.g.,AddCommand) which theAddressBookParserreturns back as aCommandobject. - All
XYZCommandParserclasses (e.g.,AddCommandParser,DeleteCommandParser, ...) inherit from theParserinterface so that they can be treated similarly where possible e.g, during testing.
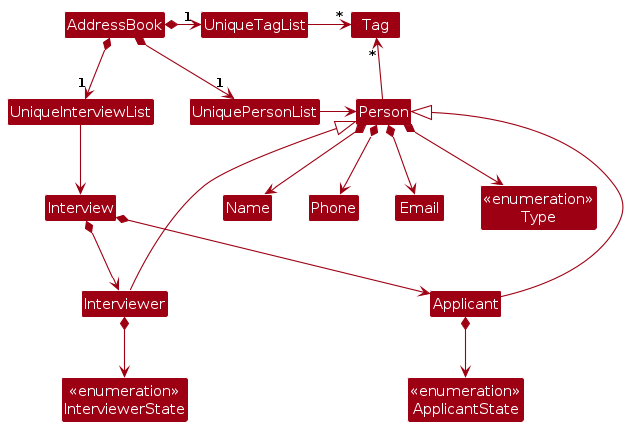
Model component
API : Model.java
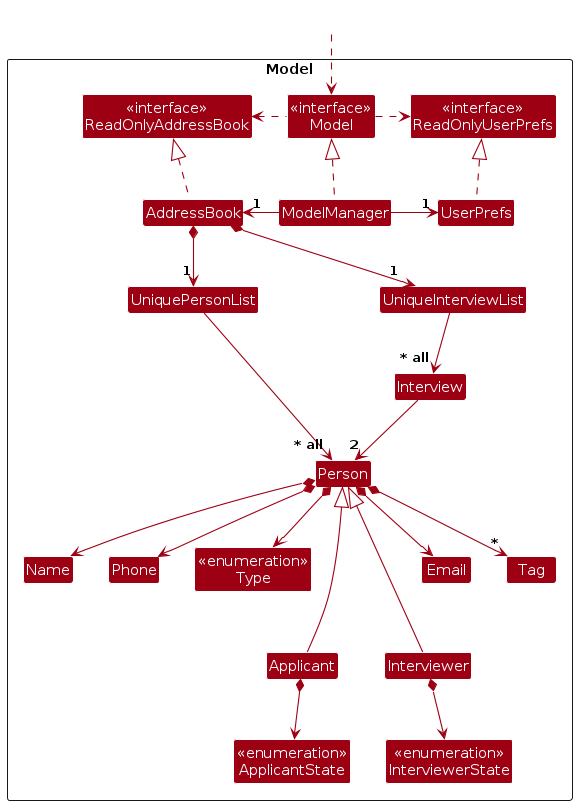
The Model component,
- stores the address book data i.e., all
Personobjects (which are contained in aUniquePersonListobject). - stores the currently 'selected'
Personobjects (e.g., results of a search query) as a separate filtered list which is exposed to outsiders as an unmodifiableObservableList<Person>that can be 'observed' e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list change. - stores a
UserPrefobject that represents the user’s preferences. This is exposed to the outside as aReadOnlyUserPrefobjects. - stores the address book data i.e., all
Interviewobjects (which are contained in aUniqueInterviewListobject). - stores the currently 'selected'
Interviewobjects (e.g., results of a search query) as a separate filtered list which is exposed to outsiders as an unmodifiableObservableList<Interview>that can be 'observed' e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list change. - does not depend on any of the other three components (as the
Modelrepresents data entities of the domain, they should make sense on their own without depending on other components)
Note: An alternative (arguably, a more OOP) model is given below. It has a Tag list in the AddressBook, which Person references. This allows AddressBook to only require one Tag object per unique tag, instead of each Person needing their own Tag objects.
Storage component
API : Storage.java
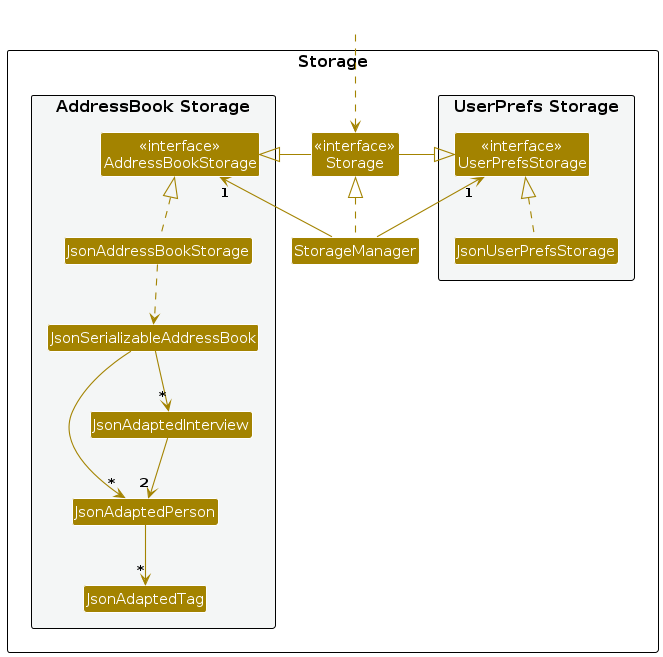
The Storage component,
- can save both address book data and user preference data in JSON format, and read them back into corresponding objects.
- inherits from both
AddressBookStorageandUserPrefStorage, which means it can be treated as either one (if only the functionality of only one is needed). - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent (because theStoragecomponent's job is to save/retrieve objects that belong to theModel)
Common classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the seedu.addressbook.commons package.
Implementation
This section describes some noteworthy details on how certain features are implemented.
Interviews
Implementation
An interview contains the following fields: Date, Start time, End time, Description, and two Person instances representing the applicant and interviewer.
Find feature
Implementation
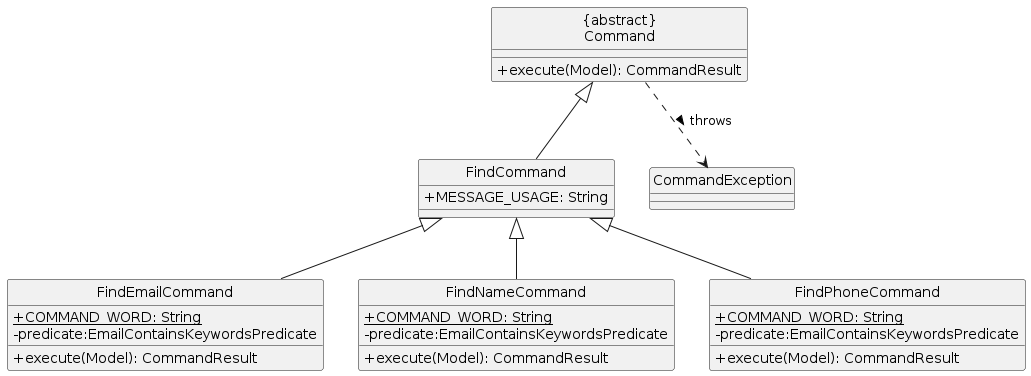
The find mechanism is facilitated by 3 classes FindEmailCommand, FindNameCommand and FindPhoneCommand. They all extend FindCommand with their corresponding COMMAND_WORD : find_email, find_name and find_phone respectively, as well as a corresponding predicate variable of type EmailContainsKeywordsPredicate, NameContainsKeywordsPredicate and PhoneContainsKeywordsPredicate respectively.
EmailContainsKeywordsPredicate, NameContainsKeywordsPredicate and PhoneContainsKeywordsPredicate extend Predicate from the java.util.function package and override the test function to match their respective criteria of matching Email, Name and Phone values respectively.
These Predicate objects allow for matching of multiple substrings, facilitating searching for multiple persons in the application simultaneously. This is done by providing multiple keyword arguments after the find_[email/name/phone] command word. However, this only applies to keywords for the same criteria.
Example: Keyword arguments after find_name will be matched only to the Name values of persons in application data, and not theie Email or Phone values.
FindEmailCommand#execute()— Searches for persons based on the specified email keywords.FindNameCommand#execute()— Searches for persons based on the specified name keywords.FindPhoneCommand#execute()— Searches for persons based on the specified phone keywords.history.
The above execute operations utilise ModelManager#updateFilteredPersonList() implemented from the Model interface to update the GUI to display the persons that match the criteria provided as arguments to the FindCommand variant.
The following class diagram summarizes the organisation of the FindCommand variant classes.
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the find mechanism behaves at each step. All 3 variants behave in the same way, just with their keywords being of different types.
Step 1. The user launches the application which loads in data from the previous session. Current data in the application include 2 Applicant objects, one with Name = "Ryan" and the other with Name = "Wesley".
Step 2. The user executes find_name command to find a person with the name Ryan in the application. The find_name command calls FindNameCommandParser#parse(), creating a new FindNameCommand object initialised with a NameContainsKeywordsPredicate object that is created with an array of the keywords passed as arguments with the find_name command. When FindNameCommand#execute() is called, the list displayed on the GUI will be updated to show only the entry of Ryan:Applicant.
Note:
- The command expects at least 1 argument following the
find_namecommand word and will result in anParseExceptionindicating invalid command format otherwise. - Use the command
list_personsto display the original list of all persons on the GUI - There is no need to return back to the original list before executing another
find_[email/name/phone]command
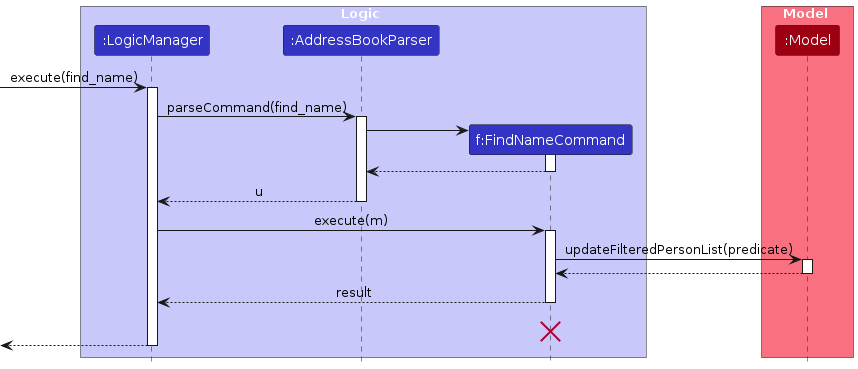
The following sequence diagram shows how a find operation, specifically `find_name`, goes through the `Logic` component. `find_phone` and `find_email` also behave in a similar way.
Design considerations:
Aspect: How find is implemented:
Alternative 1 (current choice): 3 separate commands for phone, email, and name.
- Pros: Easy and straightforward to implement.
- Cons: Uses 3 separate command words resulting in 3 separate CommandParser classes.
Alternative 2: Command word remains as
findand the first argument after will determine the criteria to search for:email,nameorphone.- Pros: Less repeating of similar code. Only 1 command word required.
- Cons: More changes to parsing is required for identification of criteria and potential errors with mixing up keywords with criteria word.
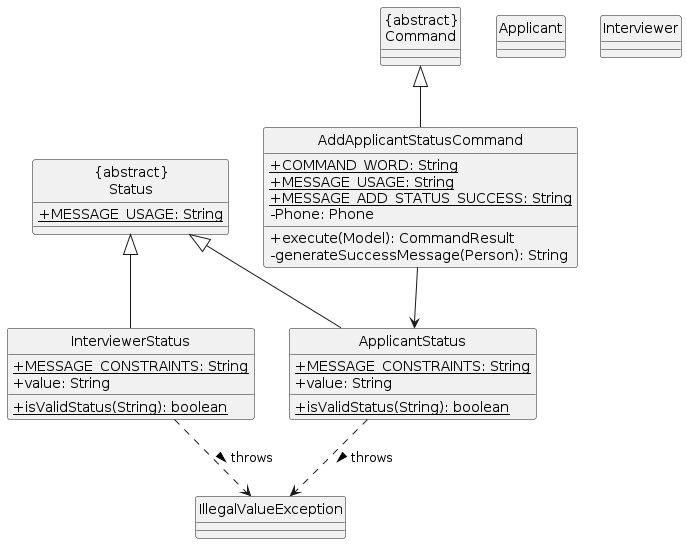
Applicant status feature
Implementation
Applicant Status
The applicant status mechanism is facilitated by AddApplicantStatusCommand. It extends Command with its own status field, stored internally as ApplicantStatus.
ApplicantStatus encapsulates statuses (enumerated in ApplicantState) in a value field.
AddApplicantStatusCommand implements the following operations:
AddApplicantStatusCommand#execute()— Adds on the encapsulatedcurrentStatusto the applicant in question.
ApplicantStatus also enables the following functionality in Applicant:
Applicant#updateCurrentStatusToReflectScheduledInterview()— Updates thecurrentStatusof the applicant to "pending interview".Applicant#revertCurrentStatus()— Reverts thecurrentStatusof the applicant to "resume review".Applicant#getCurrentStatus()— Returns the stringified version of the encapsulatedcurrentStatuswhich is simply itsvalue"
Interviewer Status
Unlike for applicant statuses, there is no AddInterviewerStatusCommand available for users. interviewer statuses are managed only internally between Interview, InterviewerStatus and Interviewer.
Another important difference is that while an Applicant contains at most 1 currentStatus, an Interviewer contains a variable-size list of upcomingInterviews containing objects of type InterviewerStatus in the form of "interview with [applicant name]".
The interviewer status mechanism is facilitated by InterviewerStatus. It extends Status and
encapsulates statuses (enumerated in InterviewerState) in a value field represented as a String.
InterviewerStatus enables the following functionality in Interviewer:
Interviewer#updateCurrentStatusToReflectScheduledInterview()— Appends a new "interview with..." status to the list ofupcomingInterviewsof the interviewer.Interviewer#updateCurrentStatusToReflectDeletedInterview()()— Removed the specific "interview with..." status of from the list ofupcomingInterviewsof the interviewer.Interviewer#getCurrentStatus()— Returns the stringified version of the encapsulatedupcomingInterviewslist by retrieving the stringified version of each of theInterviewStatusin theupcomingInterviewslist and separating them with a newline.- Note that if an interviewer has no upcoming interviews, then instead of storing an
InterviewerStatusof "free" insideupcomingInterviews, the list is left empty andgetCurrentStatusjust returns the String "free" instead.
- Note that if an interviewer has no upcoming interviews, then instead of storing an
General Notes
The following class diagram shows the overall structure of AddApplicantStatusCommand, ApplicantStatus, InterviewerStatus:
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the applicant/interviewer status mechanism behaves at each step.
Step 1. The user launches the application for the first time and executes add_applicant n/Yash p/98362254 e/yashwit@u.nus.edu. An applicant Yash is initialised with default currentStatus "resume review".
Step 2. The user executes add_interviewer n/Ryan p/12345678 e/ryan@u.nus.edu. An interviewer Ryan is initialised with default upcomingInterviews .
Step 3. The user executes add_interview....a/98362254 i/12345678 to create an interview between Yash and Ryan. The add_interview command makes a call to updateCurrentStatusToReflectScheduledInterview in Yash, which updates Yash's currentStatus to "pending interview". Similarly, a call is made to updateCurrentStatusToReflectInterview in Ryan and Ryan's upcomingInterviews is appended with "interview with Yash". The updateCurrentStatusToReflectScheduledInterview methods in Ryan and Yash in-turn call the setPerson list of the current Model for the status change to be reflected immediately.
Note: If the add_interview command fails its execution, it will not call updateCurrentStatusToReflectScheduledInterview, so the address book state will not be modified.
Step 4. The user now decides that she wants to edit Yash's status to "completed interview" manually, and executes the applicant_status 98362254 s/completed interview command. The applicant_status command will call AddApplicantStatusCommandParser#parse(), which will verify the validity of the status through ApplicantStatus#isValidStatus() through ParserUtil before creating an ApplicantStatus and then an AddApplicantStatusCommand.
Note: If the status passed by the user matches with none of the statuses enumerated in ApplicantState, a new ApplicantStatus is not created and consequently neither is an AddApplicantStatusCommand.
The following sequence diagram illustrates step 4:
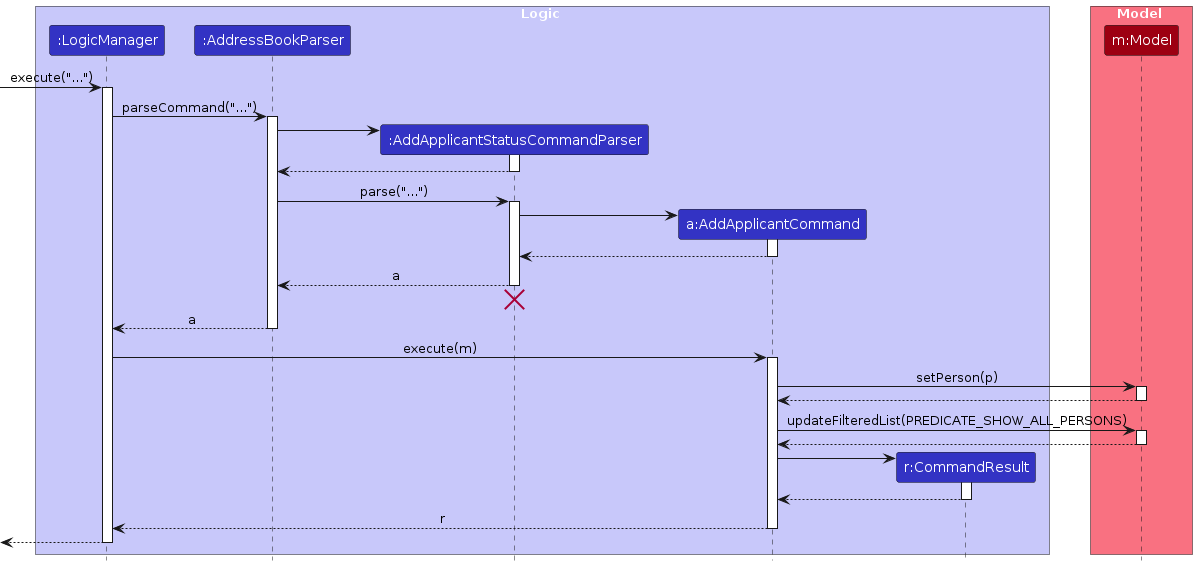
Design considerations:
Aspect: Customisability of statuses for users:
Alternative 1 (current choice): Users can only set those applicant statuses enumerated in
ApplicantState.- Pros: Less prone to user inputs that may crash the application or interfere with data integrity.
- Cons: Less freedom for users, especially those whose companies have their own set of business rules.
Alternative 2: Custom statuses.
- Pros: Can switch to pre-existing
Tagarchitecture to implement statuses since they are very similar and there is more leeway in setting tags. - Cons: Lose a bit of control over status management and degrade separation of concerns. More prone to errors when parsing user input.
- Pros: Can switch to pre-existing
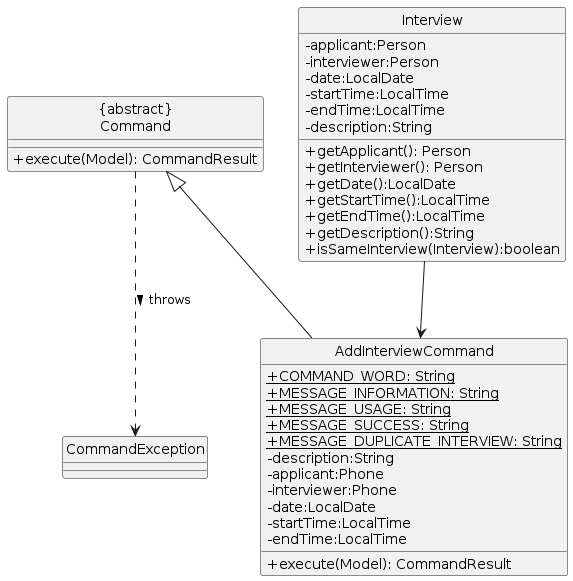
Add Interview Feature
Implementation
The add interview mechanism is facilitated by AddInterviewCommand. They all extend the Command with fields called description, applicant phone number,
interviewer phone number, date of interview, startTime as well as endTime. An Interview is created then added to the list.
AddInterviewCommand implements the following operations:
AddInterviewCommand#execute()— Adds the encapsulatedInterviewto the list.
The above execute operation utilises ModelManager#updateFilteredPersonList() implemented from the Model interface to obtain the list of applicant and interviewer phone numbers.
This is followed by checking the validity of the phone numbers before creating an Interview object to be added into the interview list. The operation execute then utilises
ModelManager#addInterview() implemented from the Model to add the Interview to the list. The operation execute also utilises ModelManager#sortInterview() to the interview objects by date, startTime and endTime.
The following class diagram summarizes the organisation of the AddInterviewCommand:
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the mechanism behaves at each step.
Step 1. The user launches the application for the first time and executes add_applicant n/Wesley p/81159858 e/ywesley16@gmail.com. An applicant Wesley is initialised.
Step 2. The user executes add_interviewer n/Yash p/98362254 e/yashwit@u.nus.edu. An interviewer Yash is initialised.
Step 3. The user executes add_interview desc/technical interview date/2024-03-28 st/10:00 et/11:00 a/81159858 i/98362254. The add_interview command calls the AddInterviewCommandParser#parse(),
creating a new AddInterviewCommand object initialised with the respective fields. When the AddInterviewCommand#excute() is called, a check is conducted to determine whether the Interview is already scheduled.
This is then followed by creating Interview object and adding it into the list. The list of interviews will then be sorted. The GUI will display the interviews under the interview column.
Note:
- The command expects all arguments to be filled and will result in
ParseExceptionindicating invalid command format otherwise. - When a duplicate interview is entered, it will result in a
CommandExceptionindicating a duplicate interview has been entered. - When incorrect phone numbers are entered, it will result in a
CommandExceptionindicating which phone number is incorrect.
The following sequence diagram shows demonstrates step 3:
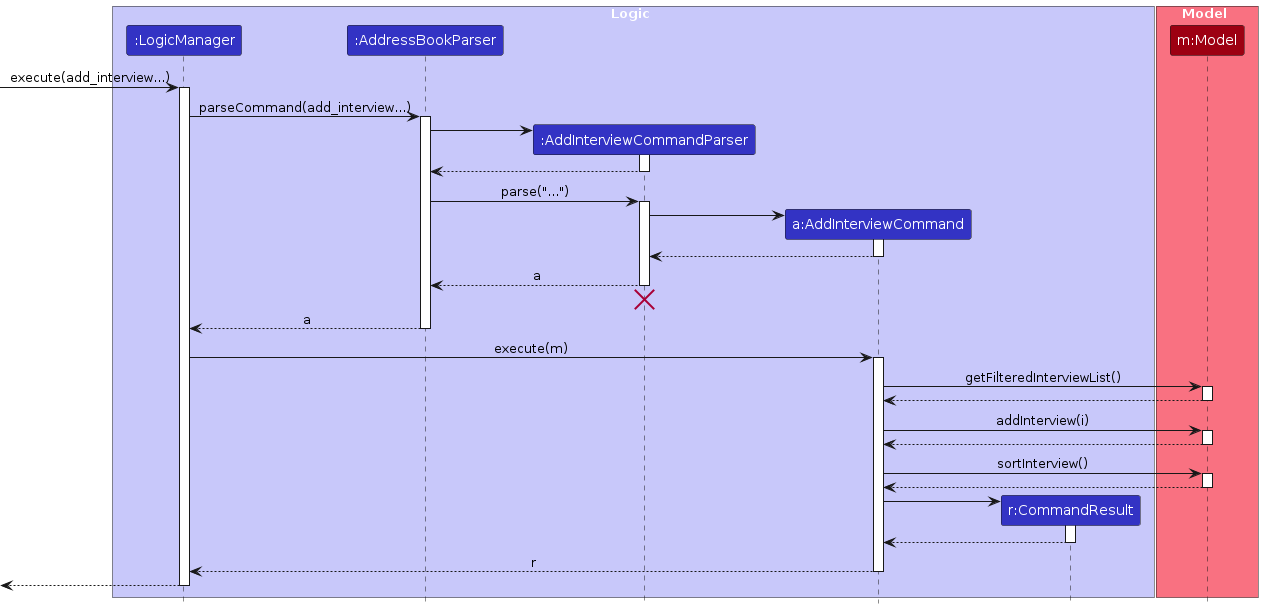
Design considerations:
Aspect: How interviews are added:
Alternative 1(current choice): Creates the
InterviewinsideAddInterviewCommand.- Pros: Easier to implement and straight forward.
- Cons: Exposes the fields and tedious to recreate
Interview.
Alternative 2:
Interviewis created underAddInterviewCommandParser.- Pros: Better encapsulation.
- Cons: Harder to conduct the necessary checks for validity for phone numbers.
Saving of interviews/persons feature
Implementation
The interview and person saving mechanism in the application is powered through the coordination of seven key components:
JsonSerializableAddressBook, JsonAdaptedStorageBook JsonAdaptedPerson, JsonAdaptedTag, JsonAdaptedInterview, LogicManager, and StorageManager.
The LogicManager triggers data persistence post-command execution by invoking StorageManager's saveAddressBook function
which in turn triggers JsonAddressBookStorage's saveAddressBook command.
This process generates a new JsonSerializableAddressBook object, encapsulating lists for both persons and
interviews.
The Model class harbors an addressBook with distinct
lists (UniquePersonList and UniqueInterviewList) for storing Person
and Interview entities. During the serialization phase, these entities are transformed into
JSON format, utilizing JsonAdaptedPerson and JsonAdaptedInterview for accurate mapping.
Each JsonAdaptedPerson retains Person attributes as @JsonProperty and encapsulates tags
as JsonAdaptedTag collections. Likewise, JsonAdaptedInterview conserves Interview attributes,
additionally incorporating applicant and interviewer information as JsonAdaptedPerson instances.
The following sequence diagram illustrates a simplified version of the above process.
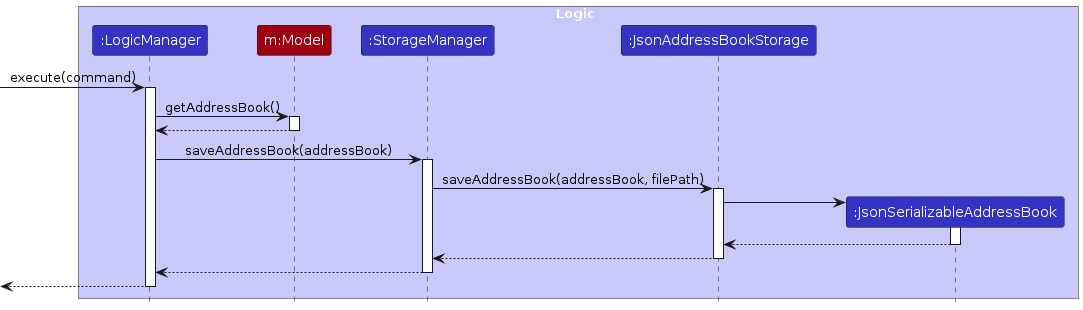
Design considerations:
Aspect: How interviews/persons are stored:
Converting person and interview data to JSON format facilitates easy data storage, retrieval, and manipulation. JSON, being lightweight and text-based, is highly compatible across different systems, making data sharing and application scaling more efficient. It also supports hierarchical data structures, which is useful for representing complex data relationships. JSON's human-readable format simplifies debugging and development processes, enhancing overall productivity.
Alternative 1(current choice): Save interviews/persons in JSON format.
Pros: Human-readable format simplifies debugging and development processes, compatible with web APIs and databases.
Cons: Harder to implement for a beginner developer.
Alternative 2: Save interview/person directly as strings.
- Pros: Easy to implement.
- Cons: Does not follow existing format, needs to reformat how saving for persons is done which could be very time-consuming, may not be compatible with exisitng APIs and databases.
List Persons and List interview Features
Implementation
The listing mechanism is facilitated by ListCommand and ListInterviewsCommand. They all extend the Command class. ListCommand is responsible for listing persons while ListInterviewsCommand is for listing interviews.
The command words for ListCommand and ListInterviewsCommand are list_persons and list_interviews respectively.
Both ListCommand and ListInterviewsCommand implements the following operations:
ListCommand / ListInterviewsCommand #execute()- Updates the list inModelwith the original list.
The above execute operation utilises ModelManager#updateFilteredPersonList() or ModelManager#updateFilteredInterviewList() respectively implemented from the Model interface, with the PREDICATE_SHOW_ALL_PERSONS Predicate, to update the list in Model with the full list.
This change is then reflected in the UI list of persons / Interviews.
The following class diagram summarizes the organisation of the two different list commands:
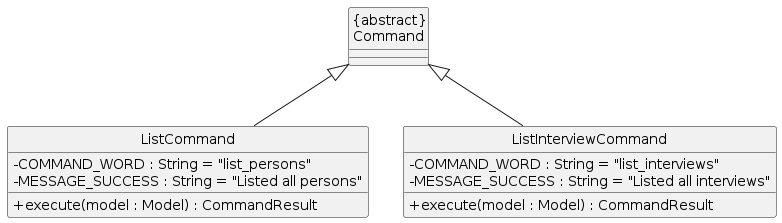
Given below is an example usage scenario for interviews and how the mechanism behaves at each step.
Step 1. The user launches the application with existing interviewers, applicants, and interviews. The interviews' date are all different.
Step 2. The user executes the command
filter_interviews_by_date 2024-02-03. Only interviews on the date2024-02-03will show up on the list of interviews on right side of the application.Step 3. Now the user wants to see the original list of interviews in step 1 (eg. All interviews, regardless of date). The user can enter the command
list_interviews. Now the list on the right side of the application will show the full list of interviews as in Step 1.
The scenario for persons is also similar to interviews.
Note:
- Both
list_personsandlist_interviewscommands have no arguments.
Delete Interview and Delete Persons feature
Implementation
The deleting mechanism for persons and interview are facilitated by DeleteCommand and DeleteInterviewCommand. They both extends from Command class. DeleteCommand is responsible for deleting a person while DeleteInterviewCommand is for deleting an interview.
The command words are delete_person and delete_interview respectively. DeleteCommand takes in a phone number to identify the person to delete, while DeleteInterviewsCommand takes in the index of the interview to delete.
Both DeleteCommand and DeleteInterviewsCommand implements the following operations:
DeleteCommand / DeleteInterviewsCommand #execute()- Removes the corresponding person or interview from the list inModel.
The above execute operation utilises ModelManager#deletePerson() or ModelManager#deleteInterview() respectively implemented from the Model interface,to remove the corresponding person or interview from the list in Model.
This change is then reflected in the UI list of persons / Interviews.
The following class diagram summarizes the organisation of the two different delete commands:
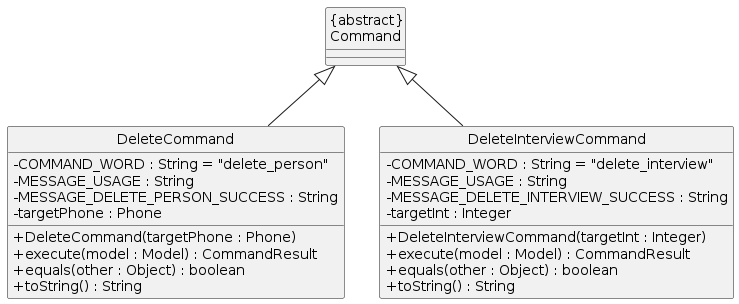
Note:
- If the argument entered (phone number or index) references a interview or person that is not in the current list, it will result in a
CommandExceptionindicating an out of bounds or invalid phone number error. - If there is no argument provided, it will result in
ParseExceptionindicating invalid command format.
Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
Appendix: Requirements
Product scope
Target user profile:
Hiring manager who:
- cannot afford a professional Applicant Tracking System (ATS)
- has a need to manage a significant number of job applicants and their interview details
- prefer desktop apps over other types
- can type fast
- prefers typing to mouse interactions
- is reasonably comfortable using CLI apps
Value proposition:
Free alternative for tracking interview datetimes, applicant contacts and their application statuses.
User stories
Priorities: High (must have) - * * *, Medium (nice to have) - * *, Low (unlikely to have) - *
| Priority | As a … | I want to … | So that I can… |
|---|---|---|---|
* * * | new user | see usage instructions | refer to instructions when I forget how to use the Tether |
* * * | user | add a new person (applicant/interviewer) | |
* * * | user | delete a person (applicant/interviewer) | remove person entries that I no longer need |
* * * | user | add a new interview | |
* * * | user | delete an interviewer | remove interview entries that I no longer need |
* * | user with many persons in Tether | find a person by name/email | locate details of a person without having to go through the entire list |
* * | user with many interviews in Tether | filter interviews by date | locate details of interviews without having to go through the entire list |
* * | user with many applicants of varying application status in Tether | record applicants' statuses | identify applicant's application progress |
* * | user with many interviewers of varying availabilities in the company | have a record of interviewer's scheduled interviews | identify which interviewers are occupied or available for interviews |
* * | user with many persons of varying application status in Tether | filter persons by status | contact all persons within a specific status group if necessary |
* | user collaborating with other Tether users | share an applicant's details | update other hiring managers on applicant details |
* | user who does not want to clutter local hard drive with files | store applicant's resume | view applicant's resume in Tether |
* | user with multiple ongoing interviews and many applicants/interviewers to track | view overall statistics of applicants/interviewers/interviews | keep abreast of the overall situation at all times |
{More to be added}
Use cases
(For all use cases below, the System is Tether and the Actor is the Hiring Manager, unless specified otherwise)
Use case: UC01 - List persons
MSS
User requests to list persons
System displays list of persons
Use case ends.
Use case: UC02 - Add a person with name, email and phone number
MSS
User requests to list persons (UC01)
User requests to add a new person to the list
System adds the person and updates the displayed list
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. Any of the given name, email, phone number are invalid.
2a1. System shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
Use case: UC03 - Delete a person by phone number
MSS
User requests to list persons (UC01)
User requests to delete a specific person in the list
System deletes the person
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. The given phone number is invalid or doesn't exist.
2a1. System shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
Use case: UC04 - Find a person by name/email/phone number
MSS
User requests to list persons (UC01)
User requests to find a specific person in the list by their name/email/phone number
System updates the list to only display the requested person
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. The given name/email/phone number is invalid.
2a1. Tether shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
Use case: UC05 - Update an applicant's status
Precondition: There is at least 1 applicant in the system.
MSS
User requests to list persons (UC01).
User requests to update a specific applicant's status
System changes the applicant's status
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. The given applicant phone number is invalid or doesn't exist.
2a1. System shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
2b. The given status is an invalid applicant status.
2a1. System shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
Use case: UC06 - Filter by status
Precondition: There is at least 1 applicant or interviewer in the system.
MSS
- User requests to list persons (UC01).
- User requests to filter by a given status
- System updates the filtered list
Extensions
2a. The given status is neither a valid applicant nor interviewer status.
2a1. System shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
Use case: UC07 - List interviews
MSS
User requests to list interviews
System shows a list of interviews
Use case ends.
Use case: UC08 - Add an interview
MSS
User requests to list interviews (UC07)
User requests to add a new interview to the list
System adds the interview and updates the displayed list
Use case ends.
Extensions
3a. Any of the given description, date, time, phone number are invalid.
3a1. System shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
Use case: UC09 - Delete an interview
MSS
User requests to list interviews (UC07)
User requests to delete a specific interview in the list
System deletes the interview
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. The list is empty.
2a1. System shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
3a. The given index is invalid.
3a1. System shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
Use case: UC10 - Filtering interviews by date
MSS
User requests to list interviews (UC07)
User requests to filter interview by a specified date
System updates the list to only display interviews that match the specified date
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. The given date is invalid.
2a1. Tether shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
2b. There are no interviews on the specified date.
2b1. Tether shows a no interviews found message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
Use case: UC11 - View overall statistics
MSS
User requests to list persons (UC01).
User requests to view overall statistics
System displays number of applicants (total, and by status), number of interviewers (total, and by status), and number of interviews
Use case ends.
{More to be added}
Non-Functional Requirements
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java 11 or above installed.
- Should be able to hold up to 1000 persons without a noticeable sluggishness in performance for typical usage.
- Should be able to display lists of persons and interviews without a noticeable sluggishness in performance for typical usage.
- Should be responsive in all functionality, especially updating and displaying the list after each request.
- Should be able to reliably preserve application data across multiple sessions without risk of data loss/corruption.
- Should not leak person details, especially email and phone number, outside the application.
- Should provide specific error messages to guide users on intended usage of features.
- A user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
{More to be added}
Glossary
- Application Status: These statuses comprise resume review, pending interview, completed interview, accepted, rejected and waiting list.
- Application Tracking System: A software application used by organizations to manage and streamline the recruitment and hiring process
- Mainstream OS: Windows, Linux, Unix, MacOS
- Person: A person can refer to either an
Applicantor anInterviewer - Private contact detail: A contact detail that is not meant to be shared with others
Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Given below are instructions to test the app manually.
Note: These instructions only provide a starting point for testers to work on; testers are expected to do more exploratory testing.
Launch and shutdown
Initial launch
Download
tether.jarand copy into an empty folderDouble-click the jar file or run
java -jar tether.jar. Expected: Shows the GUI with a set of sample contacts. The window size may not be optimum.
Saving window preferences
Resize the window to an optimum size. Move the window to a different location. Close the window.
Re-launch the app by double-clicking the jar file or running
java -jar tether.jar.
Expected: The most recent window size and location is retained.
Closing the app using the
exitcommand- Type the command exit into the command line and hit enter.
Expected: The app window closes.
- Type the command exit into the command line and hit enter.
Closing the app by clicking on the close button
- Click the close button in the top right hand corner of the app window.
Expected: The app window closes.
- Click the close button in the top right hand corner of the app window.
Closing the app by clicking on the
Exitbutton in theFiletabClick on the
Filetab in the top left corner of the app window.Click on the
Exitbutton that is displayed under theFiletab. Expected: The app window closes.
Deleting a person
Deleting a person while all persons are being shown
Prerequisites: List all persons using the
list_personscommand. Multiple persons in the list, specifically there exists a person with phone number123and there is no existing person with phone number456.Test case:
delete 123
Expected: Contact with phone number123is deleted from the list. Details of the deleted contact shown in the status message. Timestamp in the status bar is updated.Test case:
delete 456
Expected: No person is deleted. Error details shown in the status message. Status bar remains the same.Other incorrect delete commands to try:
delete,delete x,...(where x is an invalid phone number)
Expected: Similar to previous.
Finding a person
Finding a person by name
Prerequisites: Tether already contains multiple persons in the list, specifically there exists a person with name
Aliceand there is no existing person with phone numberBob.Test case:
find_name Alice
Expected: Contact with nameAliceis displayed on the list.Test case:
find_name Bob
Expected: An empty list is displayed.
Finding a person by phone number
Prerequisites: Tether already contains multiple persons in the list, specifically there exists a person with phone number
123and there is no existing person with phone number456.Test case:
find_phone 123
Expected: Contact with phone number123is displayed on the list.Test case:
find_phone 456
Expected: An empty list is displayed.
Finding a person by email
Prerequisites: Tether already contains multiple persons in the list, specifically there exists a person with phone number
alice@email.comand there is no existing person with phone numberbob@email.com.Test case:
find_email alice@email.com
Expected: Contact with emailalice@email.comis displayed on the list.Test case:
find_email bob@email.com
Expected: An empty list is displayed.
Updating applicant status
Updating an applicant's status
Prerequisites: List all persons using the
list_personscommand. Multiple applicants in the list, specifically there exists an applicant with phone number123and an interviewer with phone number321.Test case:
applicant_status 123 s/accepted
Expected: Status field of applicant with phone number123is updated with "accepted". Details of the applicant with their status is shown in the result message.Test case:
applicant_status 321 s/accepted
Expected: Status field of interviewer with phone number321does not change. Error message displayed to user stating that only applicants can be given this status.Test case:
applicant_status 123 s/free
Expected: Status field of applicant with phone number123does not change. Error message displayed to user stating that applicant status can only be given one of a given set of statuses.Test case:
applicant_status hello s/free
Expected: Error message displayed to user stating that either the command format or parameters are invalid.Test case:
applicant_status 123 s/accepted s/rejected
Expected: Status field of applicant with phone number123is updated with "rejected". Details of the applicant with their status is shown in the result message.Test case:
applicant_status 123 s/accepted rejected
Expected: Status field of applicant with phone number123does not change. Error message displayed to user stating that applicant status can only be given one of a given set of statuses.
Filtering persons by status
Filtering persons by status
Prerequisites: List all persons using the
list_personscommand. 4 applicants in the list, specifically there exists 2 applicants with statusresume reviewandpending interviewrespectively, and 2 interviewers with statusfreeandinterview with applicantOneNamerespectively.Test case:
filter_by_status resume review
Expected: Displayed list of persons is updated to show only 1 applicant with statusresume review.Test case:
filter_by_status pending interview
Expected: Displayed list of persons is updated to show only 1 applicant with statuspending interview.Test case:
filter_by_status free
Expected: Displayed list of persons is updated to show only 1 interviewer with statusfree.Test case:
filter_by_status interview with applicantOneName
Expected: Displayed list of persons is updated to show only 1 interviewer with statusinterview with applicantOneName.Test case:
filter_by_status 1
Expected: Displayed list of persons doesn't change. Error message is displayed stating invalid command format or parameters.Test case:
filter_by_status accepted
Expected: Displayed list of persons doesn't change. Message is displayed stating no persons found with the given status.
Deleting an interview
Deleting an interview while all interviews are being shown
Prerequisites: List all interviews using the
list_interviewscommand. One interview in the list.Test case:
delete 1
Expected: The only interview is deleted from the list. Details of the deleted interview shown in the status message. Timestamp in the status bar is updated.Test case:
delete 5
Expected: No interview is deleted. Error details shown in the status message. Status bar remains the same.Other incorrect delete commands to try:
delete,delete x,...(where x is an invalid phone number)
Expected: Similar to previous.
Filtering interviews by date
Filtering interviews by date
Prerequisites: Tether already contains multiple interviews in the list, specifically there exists multiple interviews with date
2024-05-05and there is no existing interview with date2024-06-06. Additionally, ensure that the original interview list is displayed by using thelist_interviewscommand.Test case:
filter_interviews_by_date 2024-05-05
Expected: Interviews with date2024-05-05is displayed on the list.Test case:
filter_interviews_by_date 2024-06-06
Expected: A message indicating that no interviews are found is displayed, and the displayed interview list does not change.
View overall statistics
View overall statistics
Prerequisites: List all persons using the
list_personscommand. 4 applicants in the list, specifically there exists 2 applicants with statusresume reviewandpending interviewrespectively, and 2 interviewers with statusfreeandinterview with applicantOneNamerespectively. List all interviews using thelist_interviewscommand. 1 interview in the list, between the same interviewer whose status isinterview with applicantOneNameand the same applicant whose status ispending interview.Test case:
view_overall_statistics
Expected: Message is displayed stating 2 applicants total (1 in resume review and 1 in pending interview), 2 interviewers total (1 free and 1 busy), and 1 interview total.Test case:
view_overall_statistics 1
Expected: Same result as Test Case 2. Extraneous parameters are ignored
Saving and Loading data from data file
Saving and loading data from data file.
Prerequisites: The data file exists and is located at
data/addressbook.json. Data in data file is valid.Perform commands that changes data in Tether (Example: add an applicant using
add_applicant n/Alice p/123 e/alice@email.com)Close and launch Tether again.
Expected: Tether correctly displays the updated data.
Dealing with corrupted data file.
Prerequisites: The data file exists and is located at
data/addressbook.json.Add an invalid character to the
addressbook.json(e.g. add a # to the start of file).Close and launch Tether again.
Expected: Tether does not display any data and an error message is shown in the terminal.
Dealing with missing data file.
Prerequisites: The data file exists and is located at
data/addressbook.json.Delete the data file located at
data/addressbook.json.Close and launch Tether again.
Expected: New data file created atdata/addressbook.jsoncontaining some sample data.
Appendix: Planned Enhancements
Team Size: 5 members
Given below are the planned enhancements we plan to implement for our application in the future:
Add group/panel interviews
- Description: Currently, each interview can only have one applicant and one interviewer. This can be problematic since it is common for group interviews to occur where there are multiple interviewers/applicants in one interview.
- Enhancement: To resolve this, we plan to allow the
add_interviewcommand to take in more than one applicants/interviewers phone number. - Example: The user can add two applicants and 2 interviewers to an interview by executing
add_interview desc/Group interview date/2024-05-05 st/13:00 et/15:00 a/11111111 a/22222222 i/33333333 i/44444444.
AddApplicantStatusCommandto accommodate custom statuses- Description: Currently, the
AddApplicantStatusCommandstrictly checks if the status given by the user matches any of 5 preset statuses. This can be problematic since different companies may have different conventions on applicant statuses and thus require adding applicant statuses to be more flexible. - Enhancement: To resolve this, we plan to change the
AddApplicantStatusCommandto accommodate custom statuses so long as they still adhere to some basic constraints such as being alphanumeric or ASCII-characters. - Example: A user may choose to execute
applicant_status 12345678 s/Stage1instead ofapplicant_status 12345678 s/resume review, depending on their specific label for the first stage of the hiring pipeline.
- Description: Currently, the
Shorthand for commands
- Description: Currently, some commands can be very long and take some to type out. This can affect the efficiency of the hiring manager.
- Enhancement: To resolve this, we plan to add shorter versions of existing commands by modifying the parser classes to take in these shorter commands.
- Example: User can filter interviews by
fibd 2024-05-05instead of typing out the wholefilter_interviews_by_date 2024-05-05.
PersonCardto accommodate dynamic sizing- Description: Currently, the
PersonCardencapsulating all the fields of a person (name,email,status...) spills out of bounds when the fields have too long values or when statuses stack up vertically (for interviewers). This can be problematic since it impedes the user view of the application and undermines their interaction with it. - Enhancement: To resolve this, we plan to calibrate the
PersonCards to be more dynamically sized i.e. resize themselves when the information they encapsulate grows out of the current dimensions.
- Description: Currently, the
Edit parameters of persons
- Description: Currently, the only way to edit a person’s details is to delete the person and re-add the person with the corrected details. This can be problematic as users have to execute multiple commands with repeated parameters just to make a small change.
- Enhancement: We plan to abstract these steps into a single edit command which allows users to change specific parameters of a selected person.
- Example: Assuming the first person in the list has name Alice and the user wants to change the person’s name to Bob, the command
edit 1 n/Bobcan be executed.
Tagging persons
- Description: Currently, applicant and interviewer tags are automatically added when a person object is created and cannot be modified. This can be inconvenient for users who may want to manually append additional information in the tags of existing people, but are unable to do so in the current iteration of Tether.
- Enhancement: To resolve this, we plan to modify the currently private add tag functionality into a command that users can input in the command box to add custom tags to persons.
- Example: Users can now execute
tag 1 lateto add a late tag to the first person in the list.
More specific error messages
- Description: Some of the commands currently are not the most specific when it comes to error messages. Users who enter the parameters wrongly might not be able to tell from a glance what went wrong. One example would be for the add_interview command if the user accidentally swapped the interviewer and applicant’s phone numbers.
- Enhancement: We can create a new exception for when the user swaps the interviewer and applicant’s phone numbers.
- Example: If the phone numbers are swapped, an error message will be shown: “You seemed to have swapped the interviewer and applicant’s phone numbers”.
Separate Applicant/Interviewer list
- Description: Currently, all persons (regardless of applicant or interviewer) are packed in the persons list, with their respective tags. These two different types of persons are not sorted or separated. This might not be convenient when you only want to look at either applicants or interviewers but not both.
- Enhancement: We can modify the UI to have a third list, of Interviewers, in the middle. The leftmost list will be list of Applicants, while the rightmost will remain to be the list of interviews. The two persons list will be labelled Applicants and interviewers respectively.
- Example: The two different lists will be as described, then the list_persons command will reset all filters for both lists. find_name/phone/email command will also work for both. The Applicant and Interviewer Tag is no longer shown.
Delete Interviews when deleting a person
- Description: Currently, when the user tries to delete a person, the system checks whether that person is involved in any existing interviews (be it as an applicant or interviewer). If this is false, the command executes as normal. However, if it is true, the command execution will be blocked and the user will receive a system message stating that he or she will need to delete all interviews corresponding to the person before he or she can delete the person. This might be troublesome if there are many interviews to be deleted.
- Enhancement: We plan to add a cascading function that will automatically search for all existing interviews corresponding to the person and delete them, as well as the person. We will also ask the user to confirm this action before proceeding.
- Example: If applicant A has 3 existing interviews, when the user deletes this applicant, the system will ask for confirmation first. After confirming, the application will delete applicant A together with all 3 interviews corresponding to A.
Delete multiple people at once
- Description: Currently, the user can only delete one person at a time. This may be problematic because the user may want to delete many people at once and this can take up quite some time.
- Enhancement: We plan allow the
delete_personcommand to take in multiple phone numbers at once. - Example: The user can execute
delete_person 11111111 22222222 33333333to delete persons with the respective phone numbers.
Appendix: Effort
Challenges :
- Designing and implementing the
addInterviewCommandfrom scratch. - Getting the GUI to display a separate list for interviews and ensuring it did not distort other current GUI components.
- Saving of
InterviewandPersontogether in the same JSON file with no issues. - Implementing multi status for
Interviewer.
Effort Required and Difficulty :
- 2 new sub-entity types (
Applicant,Interviewer) extending AB3's 1 entity type (Person). - 1 new entity type (
Interview). - 3 new data type (
Remark,Type,Status). - 12 new commands (AB3 only had 8 commands of which we removed 2 and updated 3 commands).
- Updated UI to accommodate to
PersonandInterview- 2 list panels compared to 1 in AB3.